

DEMOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICS
Demographic Characteristics
According to the 2021 Population and Housing Census, Ayawaso West Municipal Assembly had a population of 75,303 representing 1.4% of Greater Accra Region’s population of (5,455,692) with a growth rate of 2.9.
The females (36,689) formed 48.7% of the population as against (38,614) 51.3% males, denoting more males than females in the Municipality. Comparing the 2021 Population and Housing Census (75,303) to the 2010 Population and Housing Census (70,667) there has been a decrease by 0.4 % growth rate in population in Municipality.
However, the above-mentioned figure does not reflect the true population size of the Municipality as portions of lands forming Ayawaso West was assigned to GA East, Okaikwei North and Ayawaso Central Municipal Assemblies. Ghana Statistical Service has formally acknowledged this concerned raised by the Assembly and is working to rectify it. Table 1.3 below shows the projected populations for the plan period.

Environment
Natural Resource Endowment The Municipality has no minerals to boast of. Also, as a result of the urbanisation the Municipality has lost most of its arable land, biodiversity, vegetation, water bodies and Wetlands. Currently there is very little arable land to be utilized. The remaining few are being utilized for vegetable growing and horticulture.
This form of urban Agriculture is very common in the Municipality and provides livelihoods for farmers and traders involved.
Air, Water and Land Pollution
The Municipality has lost vegetation; wildlife and wetlands due to rapid expansion of built-up spaces as a result of urbanization. Challenges in perennial flooding, waste management and pollution of water bodies with rubbish and waste water also exist. Air pollution caused by various vehicles on the roads contributes to high exhaust fumes in the atmosphere.
Noise from churches and loud music from bars, restaurants and other entertainment centre’s also cause nuisance. The Assembly will intensify efforts at sensitization and enforcement of Bylaws to curb all forms of nuisance and pollution during the plan period to provide a healthy environment for residents
Settlements and another built environment
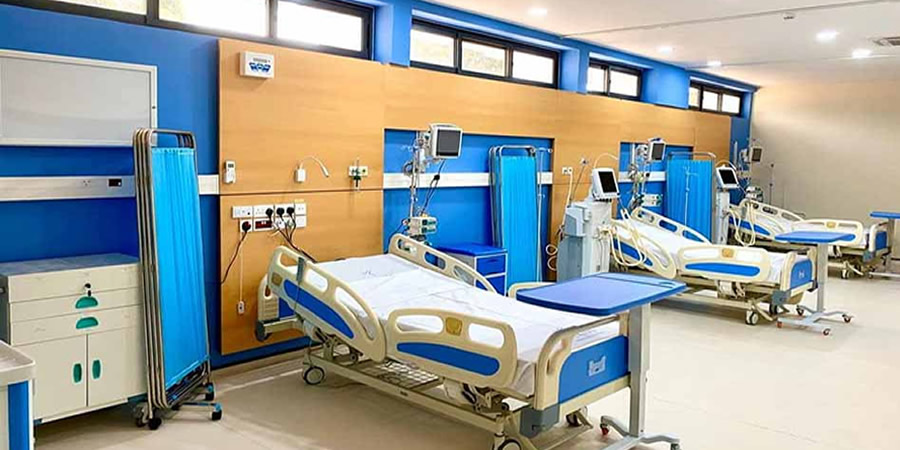
The Municipality has an urban settlement pattern with most services and infrastructure relating to education, health, banking, security, business, leisure etc. available. The mostly residential and civic settlement pattern of the Municipality has changed over the years.
This is due to increased commercial activities especially in the service industries like Hotels, Retail Outlets Banks, Cooperate institutions, etc. The Settlement pattern that has evolved is therefore mixed use in most parts of the Municipality. About 80% of roads in the Municipality are tarred. Cement blocks/concrete happens to be the widely used construction materials in the municipality with increasing high-rise buildings appearing on the landscape.
There are few unplanned areas usually in indigenous settlements and also increasing incidence of unauthorized structures. Encroachment is also a challenge in the Municipality, areas zoned for public facilities such as roads; drains and Green Belt amongst others have been encroached.
This situation poses a challenge for development control and the Assembly will therefore intensify enforcement of the building regulations and also involve all stakeholders in enforcing the building laws. The distribution of services by settlement in the Municipality is analysed using the scalogram in Table1.9 below.
Legon has been indicated with the highest settlement with functionality and first on the scalogram. This implies that Legon provides more to the functionality of Municipality than any other area. Access to services in most areas is quite good with little variation amongst areas. Most of these functions provided by Legon are accessible to all residents.

According to the 2021 Population and Housing Census, Ayawaso West Municipal Assembly had a population of 75,303 representing 1.4% of Greater Accra Region’s population of (5,455,692) with a growth rate of 2.9.
The females (36,689) formed 48.7% of the population as against (38,614) 51.3% males, denoting more males than females in the Municipality. Comparing the 2021 Population and Housing Census (75,303) to the 2010 Population and Housing Census (70,667) there has been a decrease by 0.4 % growth rate in population in Municipality.
However, the above-mentioned figure does not reflect the true population size of the Municipality as portions of lands forming Ayawaso West was assigned to GA East, Okaikwei North and Ayawaso Central Municipal Assemblies. Ghana Statistical Service has formally acknowledged this concerned raised by the Assembly and is working to rectify it. Table 1.3 below shows the projected populations for the plan period.
Environment
Natural Resource Endowment The Municipality has no minerals to boast of. Also, as a result of the urbanisation the Municipality has lost most of its arable land, biodiversity, vegetation, water bodies and Wetlands. Currently there is very little arable land to be utilized. The remaining few are being utilized for vegetable growing and horticulture.
This form of urban Agriculture is very common in the Municipality and provides livelihoods for farmers and traders involved.
Air, Water and Land Pollution
The Municipality has lost vegetation; wildlife and wetlands due to rapid expansion of built-up spaces as a result of urbanization. Challenges in perennial flooding, waste management and pollution of water bodies with rubbish and waste water also exist. Air pollution caused by various vehicles on the roads contributes to high exhaust fumes in the atmosphere.
Noise from churches and loud music from bars, restaurants and other entertainment centre’s also cause nuisance. The Assembly will intensify efforts at sensitization and enforcement of Bylaws to curb all forms of nuisance and pollution during the plan period to provide a healthy environment for residents
Settlements and another built environment
The Municipality has an urban settlement pattern with most services and infrastructure relating to education, health, banking, security, business, leisure etc. available. The mostly residential and civic settlement pattern of the Municipality has changed over the years.
This is due to increased commercial activities especially in the service industries like Hotels, Retail Outlets Banks, Cooperate institutions, etc. The Settlement pattern that has evolved is therefore mixed use in most parts of the Municipality. About 80% of roads in the Municipality are tarred. Cement blocks/concrete happens to be the widely used construction materials in the municipality with increasing high-rise buildings appearing on the landscape.
There are few unplanned areas usually in indigenous settlements and also increasing incidence of unauthorized structures. Encroachment is also a challenge in the Municipality, areas zoned for public facilities such as roads; drains and Green Belt amongst others have been encroached.
This situation poses a challenge for development control and the Assembly will therefore intensify enforcement of the building regulations and also involve all stakeholders in enforcing the building laws. The distribution of services by settlement in the Municipality is analysed using the scalogram in Table1.9 below.
Legon has been indicated with the highest settlement with functionality and first on the scalogram. This implies that Legon provides more to the functionality of Municipality than any other area. Access to services in most areas is quite good with little variation amongst areas. Most of these functions provided by Legon are accessible to all residents.
Date Created : 11/12/2025 12:00:00 AM











 facebook
facebook
 X
X
 Youtube
Youtube
 instagram
instagram
 +233 593 831 280
+233 593 831 280 0800 430 430
0800 430 430 GPS: GE-231-4383
GPS: GE-231-4383 info@ghanadistricts.com
info@ghanadistricts.com Box GP1044, Accra, Ghana
Box GP1044, Accra, Ghana